The arthrosis of the knee joint is a chronic (long -term) degenerative disease that causes the destruction of the cartilage in the joints.Symptoms include pain, rigidity and swelling.Treatment options to reduce pain and disability include changes in lifestyle (diet, physical exercises), physical and professional treatment methods, medicines and surgery.
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint
The osteoarthritis of the knee joint is a common disease, accompanied by chronic and exhausting pain.Recent clinical data have shown that central awareness stimulates the deformation of osteoarthritis of the knee joint.A better understanding of how the arthrosis of the knee joints affects the central processing of pain is crucial for the identification of new analgesic objectives/new therapeutic strategies.
The inhibitory receptors weaken the function of peripheral immune cells and modulate the central neuroimmune responses.The systemic introduction of the receptor's agatte player has weakened the behavior of the pain induced by the OA and in this model the changes in circulating and anti -inflammatory cytokines have been manifested.
Deform arthrosis
The deforming arthrosis of the knee joint is the inflammation and wear of the cartilage on the bones that form the articulation of the knee (osteo = bone, artro = joint, itis = inflammation).The diagnosis of osteoarthritis of the knee joint is based on two main results: radiographic data on the changes in the health of the bones (using medical images, such as radiography and image of magnetic resonance imaging of magnetic resonance imaging) and human symptoms.About 14 million people have symptomatic knee arthrosis.Although the most common in the elderly, 2 million people with a symptomatic or knee or less than 45 years old during the diagnosis and more than half were younger than 65 years of age.
Osteoarthritis (knee oa) is a progressive disease caused by inflammation and degeneration of the knee joint, which over time worsens.
This affects the entire joint, including bones, cartilage, ligaments and muscles.Its development is influenced by age, by body mass index (BMI), bone structure, genetics, muscle strength and level of activity.The knee or can also develop as a secondary state after the knee injury.Depending on the stage of the disease and the presence of injuries or conditions associated with it, the knee or can be controlled using physical therapy.More serious or expanded cases may require surgery.
Symptoms
People who develop knee oa can experience a wide range of symptoms and restrictions based on the development of the disease.Pain occurs when the cartilage that covers the bones of the knee joint is worn out.The areas where the cartilage consumes or damages, exposes the bone below.The effect of the bone allows you to increase the stress and compression of the cartilage and sometimes bone contact when moving, which can cause pain.Since the knee is an articulation, the level of activity, the level of activity, as well as the type and duration of the actions, as a rule, have a direct effect on the symptoms.Symptoms can deteriorate with weight activity, for example, when walking with a heavy object.
The symptoms of knee joint can include:
- Deterioment of pain during or after surgery, especially when walking, climb, walk down the stairs or move from a seat in an upright position.
- Pain or rigidity after sitting with a folded or straight knee for a long period of time.Pain is the most common symptom of osteoarthritis.As the disease develops and inflammation, pain can become constant.
- A feeling of jumping, breaking or grinding when moving the knee.
- Swelling after action.
- The rigidity of the articulation concerned has often been seen first in the morning and after rest.
- The edema, which is sometimes hot to the touch, can be evident in the arthritis joint.
- Deformation can occur with arthrosis due to bone growth and cartilage loss.The growth of the bones in the final joints of the fingers is called Hyberden knots.Babbar's nodes are the growth of the bones in the central joints of the fingers.The degeneration of the cartilage of the knee joint can lead to the external curvature of the knees (onion foot).
- A cracker sound or a sensation of grid can be seen when the arthritis moves.This is caused by canceling the bone against the bone or rough cartilage.
Usually these symptoms do not suddenly present themselves and all at once, but develop gradually over time.Sometimes people do not admit they have osteoarthritis, because they cannot remember a certain time or injuries that have caused their symptoms.If knee pain has deteriorated for several months, which does not respond to rest or change of activity, it is better to ask for advice to a medical worker.
Diagnostics
Osteoartrosis can often be diagnosed by its characteristic symptoms of pain, reduced movement and/or deformation.Osteoarthritis can be confirmed by the X -ray or scan of magnetic resonance imaging.General data include the narrowing of the joint space between the bones, the loss of cartilage and the bone spurs or the growth of the bones.Blood exams can be used to exclude other possible conditions, but cannot diagnose arthrosis.
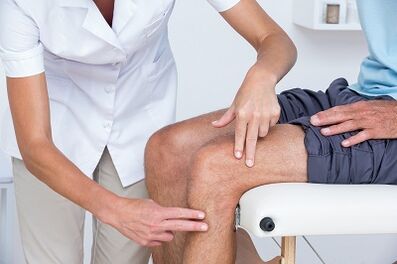
In the knee or, 2 primary processes are diagnosed.The first is based on a relationship on symptoms and clinical examination.The physiotherapist will ask questions about history and medical activity.The therapist will carry out a physical examination to measure the movement of the knee (movement interval), strength, mobility and flexibility.They can also ask for various movements to see, increase or reduce pain.
The second tool used to diagnose the knee joint is a diagnostic display.The physiotherapist can send to the doctor who will prescribe the knee X -rays in various positions to check the damage to the bone and cartilage of the knee joint.
If more serious damage to the joints are suspected, it is possible to order a magnetic resonance imaging to study more carefully the general state of joint and surrounding tissues.
Blood exams can also be ordered to help exclude other conditions that can cause symptoms similar to the osteoarthritis of the knee joints.
Treatment
Depending on the severity of arthritis and the age of the patient, it will be chosen how to treat the arthrosis of the knee joints.The treatment can consist of operating or conservative methods or their combinations.
The first line of treatment of arthritis of the knee joint includes the modification of the activity, anti -inflammatory drugs and weight loss.
The refusal of actions that improve pain can make this condition acceptable for some people.Anti -inflammatory drugs help to relieve inflammation that can contribute to pain.
Physical therapy to strengthen the muscles around the knee can help absorb part of the shock given to the joint.This is particularly true for arthritis with a cup of knee (patello-femoral).Special types of stapled brackets designed to transfer the load to the knee joint part, which is lower than arthritis, they can also relieve pain.Drug injections within the knee joint can also be helped temporarily.
In addition, walking with a stick in the hand on the opposite side, since a painful knee can help distribute part of the load, reduces the pain.Finally, weight loss helps to reduce the strength that passes through the knee joint.The combination of these conservative measures can help relieve pain and prevent disability.
If these methods do not allow to make the conditions tolerant, the operation may be the best option for the treatment of arthritis of the knee joint.The exact type of operation depends on age, anatomy and the main state.Some examples of surgical options for the treatment of arthritis include osteotomy, which consists in cutting the bone to align the articulation.
Modern methods of treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint include osteotomy, which is a good alternative if the patient is young and arthritis is limited by an area of the knee joint.This allows the surgeon to reconstruct the knee in order to download the arthritis area and carry out the load relatively not involved parts of the knee joint.For example, the patient can be reconstructed to redistribute the load through the joint.The advantage of this type of surgery is that the patient's knee joint is preserved and can potentially guarantee many years of relief from pain without the deficiencies of the prosthetic knee.The disadvantages include a longer rehabilitation course and the possibility of developing arthritis in a recently leveled knee.
The operation to replace the knee joint includes the cutting of the arthritic bone and the insertion of the prosthetic joint.All arthritic surfaces are replaced, including the cup of femur, leg and knee.The arthritic surfaces are removed and the ends of the bone are replaced by a prosthesis.The prosthetic component is generally made of metal and plastic surfaces, designed to slide smoothly against each other.
Replacement of the knee joint
The general operation to replace the knee joint was performed for the first time in 1968 and over the years it has evolved on a reliable and effective way to get rid of pain when turning off and allows patients to resume their active life.The improvements in the field of surgical methods and plants have contributed to making this most successful orthopedic procedures today.As the population ages and remains more active, the need for a general replacement of the knee continues to grow.Many operations to replace the knee joint took place in the special surgery hospital.The improvements of surgical technology and the design of new plants are some of the contributions made.
People often wonder when and why they should replace the knee.This is an individual question that depends on the level of human activity and functional needs.Many people with arthrosis live with pain, who prevents them from participating in the activities;Others are so weakened that it is difficult for them to wear shoes and socks.A complete replacement of the knee joint offers the solution to the problem of arthrosis and is performed to relieve pain and resume the activity.After rehabilitation from the successful replacement of the knee joint, the patient can expect surgery, without pain.A complete replacement of the knee joint significantly improves the patient's condition and significantly reduces its long -term treatment costs.This study has shown that not only the overall replacement of the knee joint is economically effective, but also provides greater features and the best quality of life.
A complete replacement of the knee joint is considered an important operation and the solution is not trivial.Usually people decide to undergo an operation when they feel they can no longer live with their arthritis.
The plant consists of 4 parts: tibia, parts of the femur, plastic insert and a reason.The components of the tibia and the femur are made of metal, usually cobalt chromium, are used to close the ends of the thigh and the lower part of the leg after removing the arthritic bone.The plastic insert is made of ultra -alta molecular mass polyethylene and fits into the component of the tibia, so that the surface of the polished thigh along the plastic.The component of the knee cup also slips against the front of the femoral component.They are usually attached to bone concrete.
The full replacement of the knee is performed in the operating room with a special laminar air flow system, which helps to reduce the probability of infection.Your surgeon will wear a "space", also designed to reduce the probability of infection.The entire surgical team will be composed of your surgeon, two to three assistants and nanny.
Anesthesia is administered through an epidural catheter, which is a small tube inserted in the back.During the operation, the patient can be awake and sleepy.
After the introduction of the epidural block around the thigh, a hemostatic lace or bracelet will be positioned.The horizontal bar will be overrated during the operation to reduce blood loss.The cutout for the complete replacement of the knee is made along the front knee.The incision will be measured from 4 to 10 inches depending on the anatomy.
The arthritic surfaces of the femur, the lower legs and the patella are exposed and removed using resistance tools.At the same time, the knee deformations are corrected and, after the operation, the knee becomes more straight.The bone is ready to take an artificial knee joint, then a prosthesis is inserted.During the closure, two drainage are installed around the work area to help in the evacuation of the blood.Sader are used to close the skin.
The entire operation will require 1 to 2 hours.Subsequently, the patient will be brought to the recovery room where the tests will be checked.Most patients can be brought to a normal room for several hours;Others will have to stay in the recovery room, as defined by a surgeon and a anesthesiologist.
Patients usually remain in the hospital for 3-4 days after complete operation to replace the knee
Risks during surgery
Some of the risks of the surgical procedure include blood loss, the formation of a clot in the leg and the probability of infection.The general prevalence of these risks is very small.They should be discussed with the surgeon before the start of the operation.
Some of the risks of the presence of a prosthetic knee include the probability that the parts can weaken or wear out over time, or the prosthesis can be infected.Once again, these problems will be discussed with the surgeon.
Postoperative course
Immediately after a complete operation to replace the knee joint, the patient will fall into the recovery room.Most patients can enter a normal department after a few hours, when the sensation returns to the legs.A pain pump associated with an epidural catheter will be administered, which will allow you to control when a cure for pain is given.
On the day of the operation, it is possible to perform some exercises, as indicated by the physiotherapist, including the reduction of the quadriceps and move the legs up and down.Depending on the surgeon's preference, you can start bending the new knee immediately after the operation or the first day.The patient will be authorized to take the ice after the intervention to wet the mouth, but drink liquids or you can cause nausea.The patient will have a catheter in the bladder, so you don't have to worry about urination.As soon as the movement in the legs is restored, it will be allowed to sit, get up and take a few steps with a walking and a therapist.
The first day after the operation will be active, developed to help become more mobile.
The patient will meet physiotherapists who will instruct further exercises.In addition, they will help to stand and take a few steps with a walk.As a rule, the patient will be authorized to drink a pure liquid.
In the next few days it will be easier to move.The patient will be released by pain and urinary catheter.Pain treatment will be administered in the form of tablets.The second day after the operation, if there are signs of recovery in the intestine, it will be authorized to eat normal food.
Depending on your age, preoperative physical condition and insurance coating, the patient can be a candidate for short -term accommodation in a rehabilitation institute.Otherwise, the patient will be discharged home and the physiotherapist will come to his house to continue rehabilitation.The dispatcher will discuss these options with the patient and help him plan his return home.
A return to the activity will be led by a surgeon and therapists.As a rule, patients can walk as much as they want 6 weeks after surgery.Patients can resume movement after 6 weeks.After 8 weeks, patients can resume the game in golf and swimming;At 12 weeks they can play tennis.The surgeon will help to decide what actions can be taken.
Which physiotherapist is necessary
All physiotherapists are prepared through education and clinical experience for the treatment of various conditions or injuries:
- A physiotherapist who has experience in the treatment of people with a osteoarthritis of the knee joint and after surgery to replace the knee joint.Some physiotherapists have a practice with an orthopedic focus.
- A physiotherapist who is a certified orthopedic clinical specialist.This physiotherapist will have advanced knowledge, experiences and skills that can be applied to a state.
- You can find physiotherapists who have these and other accounting data that use magnetic resonance imaging, an online tool to help find physiotherapists with specific clinical knowledge.
General advice when you can find a physiotherapist (or any other medical service provider):
- Get recommendations from family and friends or other medical service providers;
- Turning to the clinic for admission physiotherapy, it is necessary to ask for the experience of physiotherapists in helping people with arthritis.
During the first visit with the physiotherapist, you must be ready to describe the symptoms as in more detail and report on the activities that worsen the condition.




















